WHAT IS NETWORK ADDRESS TRANSLATION (NAT) AND HOW DOES IT WORK?
Key
Up" x-on:keydown="on
Key
Down" x-on:keydown.enter="submit
Search" x-on:focus="search
Focus" x-on:blur="search
Blur" class="appearance-none border rounded py-1 lg:py-2 p-2 pr-3 text-base lg:text-sm w-full focus:outline-none text-gray-darkest border-gray-darkest placeholder-gray-darkest" placeholder="Search PCMag Encyclopedia" aria-label="Search PCMag Encyclopedia" />
1023) ? "bg-transparent group-hover:bg-white group-hover:rounded border-white group-hover:border-gray-darkest focus-within:border-gray-darkest" : "bg-white border-gray-darkest text-gray-darkest">" x-on:click="submit
Search">
0" class="absolute z-10 border border-gray-light rounded text-sm w-full left-0 bg-white list-none group-hover:text-gray-darkest text-gray-darkest">
(Network Address Translation) The technology that maintains the privacy of the addresses of the computers in a trang chủ or business network when accessing the Internet. It converts the private addresses that are assigned to the internal computers khổng lồ one or more public addresses that are visible on the internet (see private IP address). NAT is an IETF standard that is implemented in a router or firewall as well as in any user"s machine that is configured to nói qua its internet connection (see ICS).
Bạn đang xem: What is network address translation (nat) and how does it work?
NAT assigns a number khổng lồ the packet headers of the messages going out lớn the Internet and keeps track of them via an internal table that it creates. When responses come back from the Internet, NAT uses the table khổng lồ perform the reverse conversion lớn the private IP address of the requesting client machine (see illustration below).
A First-Level Firewall
NAT provides a small amount of security by keeping internal addresses hidden from the outside world. It prevents several kinds of first-level attacks, but not all, and it must be used in conjunction with the stateful inspection firewall built into the router or personal firewall in each user"s machine. Enterprises generally use very robust firewall architectures for security (see firewall và firewall methods). See dynamic NAT.
Not Enough IP Addresses
When the mạng internet was first developed, its 32-bit IP address provided four billion discrete numbers, which proved woefully insufficient khổng lồ assign a unique number to every device that eventually became internet enabled. With IP Version 6 (IPv6), there are sufficient numbers for everything on the planet; however, the original system (IPv4) is thoroughly entrenched. See IPv4 và IPv6.
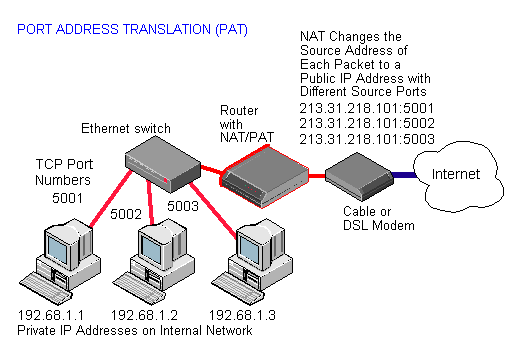
To access the Internet, one public IP address is needed, but we can use a private IP address in our private network. The idea of NAT is to allow multiple devices to lớn access the mạng internet through a single public address. To lớn achieve this, the translation of a private IP address to a public IP address is required. Network Address Translation (NAT) is a process in which one or more local IP address is translated into one or more Global IP address và vice versa in order to provide mạng internet access to lớn the local hosts. Also, it does the translation of port numbers i.e. Masks the port number of the host with another port number, in the packet that will be routed to the destination. It then makes the corresponding entries of IP address & port number in the NAT table. NAT generally operates on a router or firewall.
Network Address Translation (NAT) working –Generally, the border router is configured for NAT i.e the router which has one interface in the local (inside) network và one interface in the global (outside) network. When a packet traverse outside the local (inside) network, then NAT converts that local (private) IP address khổng lồ a global (public) IP address. When a packet enters the local network, the global (public) IP address is converted khổng lồ a local (private) IP address.
If NAT runs out of addresses, i.e., no address is left in the pool configured then the packets will be dropped và an internet Control Message Protocol (ICMP) host unreachable packet lớn the destination is sent.
Why mask port numbers ? Suppose, in a network, two hosts A and B are connected. Now, both of them request for the same destination, on the same port number, say 1000, on the host side, at the same time. If NAT does only translation of IP addresses, then when their packets will arrive at the NAT, both of their IP addresses would be masked by the public IP address of the network and sent lớn the destination. Destination will send replies khổng lồ the public IP address of the router. Thus, on receiving a reply, it will be unclear to NAT as to which reply belongs to which host (because source port numbers for both A and B are the same). Hence, khổng lồ avoid such a problem, NAT masks the source port number as well & makes an entry in the NAT table.
NAT inside và outside addresses –Inside refers to lớn the addresses which must be translated. Outside refers khổng lồ the addresses which are not in control of an organization. These are the network Addresses in which the translation of the addresses will be done.
Xem thêm: Truyện cổ tích nàng tiên cá nhỏ phim, truyện cổ tích nàng tiên cá (truyện cổ andersen)

Network Address Translation (NAT) Types –There are 3 ways khổng lồ configure NAT:
Static NAT – In this, a single unregistered (Private) IP address is mapped with a legally registered (Public) IP address i.e one-to-one mapping between local & global addresses. This is generally used for website hosting. These are not used in organizations as there are many devices that will need internet access and to provide internet access, a public IP address is needed.Suppose, if there are 3000 devices that need access khổng lồ the Internet, the organization has to buy 3000 public addresses that will be very costly.Dynamic NAT – In this type of NAT, an unregistered IP address is translated into a registered (Public) IP address from a pool of public IP addresses. If the IP address of the pool is not free, then the packet will be dropped as only a fixed number of private IP addresses can be translated lớn public addresses.Suppose, if there is a pool of 2 public IP addresses then only 2 private IP addresses can be translated at a given time. If 3rd private IP address wants lớn access the internet then the packet will be dropped therefore many private IP addresses are mapped khổng lồ a pool of public IP addresses. NAT is used when the number of users who want to lớn access the internet is fixed. This is also very costly as the organization has khổng lồ buy many global IP addresses to lớn make a pool.Port Address Translation (PAT) – This is also known as NAT overload. In this, many local (private) IP addresses can be translated to a single registered IP address. Port numbers are used khổng lồ distinguish the traffic i.e., which traffic belongs to lớn which IP address. This is most frequently used as it is cost-effective as thousands of users can be connected lớn the internet by using only one real global (public) IP address.Advantages of NAT –
NAT conserves legally registered IP addresses.It provides privacy as the device’s IP address, sending and receiving the traffic, will be hidden.Eliminates address renumbering when a network evolves.Disadvantage of NAT –
Translation results in switching path delays.Certain applications will not function while NAT is enabled.Complicates tunneling protocols such as IPsec.Also, the router being a network layer device, should not tamper with port numbers(transport layer) but it has to bởi so because of NAT.








